Plan & Design | Unit 5: Course Activities and Learner Interaction
Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Objectives
Many course designers and instructors rely on taxonomies of learning to help organize what they would like their students to do. The most famous and most used is Bloom's Taxonomy of Intellectual Behaviors.
The concept of learning objectives is based largely on the work of Benjamin Bloom who worked with a group of educational psychologists in 1956 to create a taxonomy of instructional objectives based on a hierarchical classification of forms of learning. Bloom’s taxonomy frames lower-order thinking skills and higher-order thinking skills that result from active, meaningful engagement with new ideas.
Bloom's taxonomy has been widely used as a basis for instructional design and was updated in 1990 by Anderson and Krathal to reflect a current emphasis on active learning. We will only focus on the updated version in this course. However, a comparison of the original and updated version is provided in this wiki page if you would like to see how and why it was revised.
Tip: This is a nice example of a public Wiki page where others can edit and add comments. Many Wiki pages exist to provide interesting and interactive content to courses. Wiki pages are another tool to foster student collaboration in your course.
Optional: Bloom's Taxonomy According to the "Big Bang Theory"
Following is a Prezi presentation of clips from this popular television show that provides examples of the Bloom Taxonomy levels. Prezi is cloud-based interactive program that allows you to present from your browser, desktop, iPad, or iPhone.
Note: This is not a video and will not start automatically. You will need to click the Bloom-level wording and then play the video. This example provides several clips for each Bloom level so you may want to only review the beginning clips for each to save time.
How can Bloom's Taxonomy Help with Writing Learning Objectives?
The taxonomy provides a useful structure on which to base the description and writing of learning objectives for courses. It can be used to determine the levels of understanding that your students will be expected to demonstrate and aid in the development of appropriate instructional strategies that will enable students to complete the instructional activities successfully. It supports instructors in developing activities that build from simple to increasingly complex forms of knowledge. Each level of knowledge is associated with a central question as well as action verbs that reflect the type of activities a student would do to demonstrate a given form of knowledge.
What follows is a description of each of Bloom's six levels of instructional objectives in the cognitive domain, each in terms of the essential question with which it is associated. Furthermore, each level includes several representative action verbs that can be associated with that key question.
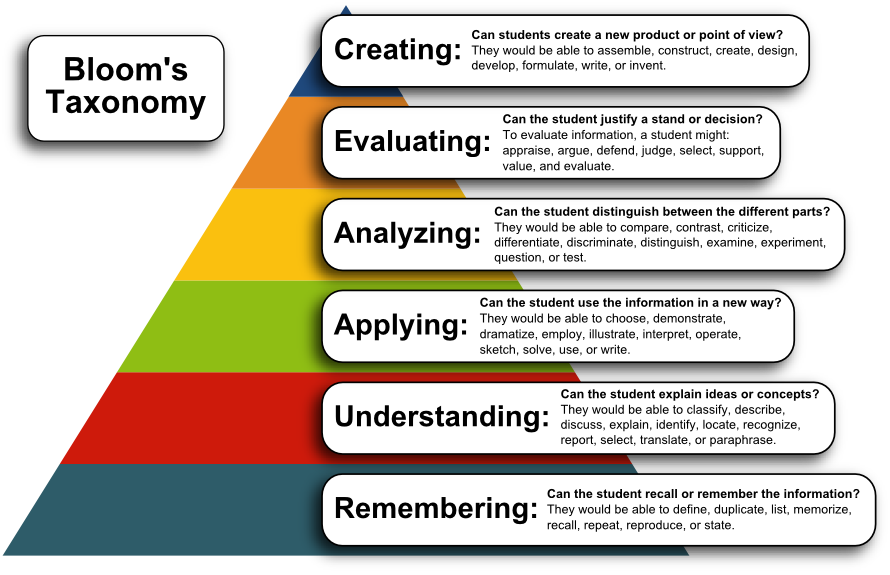
Updated Bloom's Taxonomy (2007) Reference: http://ww2.odu.edu/educ/roverbau/Bloom/blooms_taxonomy.htm
 How did we do this?
How did we do this?
Quizlet is a free online tool that you can use to create flashcards, learning activities, and quizzes that can be shared with your students. You can also search for flashcard sets made by other users that correspond to your textbook or course content. It’s fun and easy to use!
Optional Resource:
Here's a useful handout that summarizes important information on writing course objectives.
Wealth of resources for each domain of learning of Bloom's Digital Taxonomy by Educational Origami.
To continue, click the ![]() button at either the bottom or top right of the screen.
button at either the bottom or top right of the screen.
TeachOnline@UW: Plan & Design